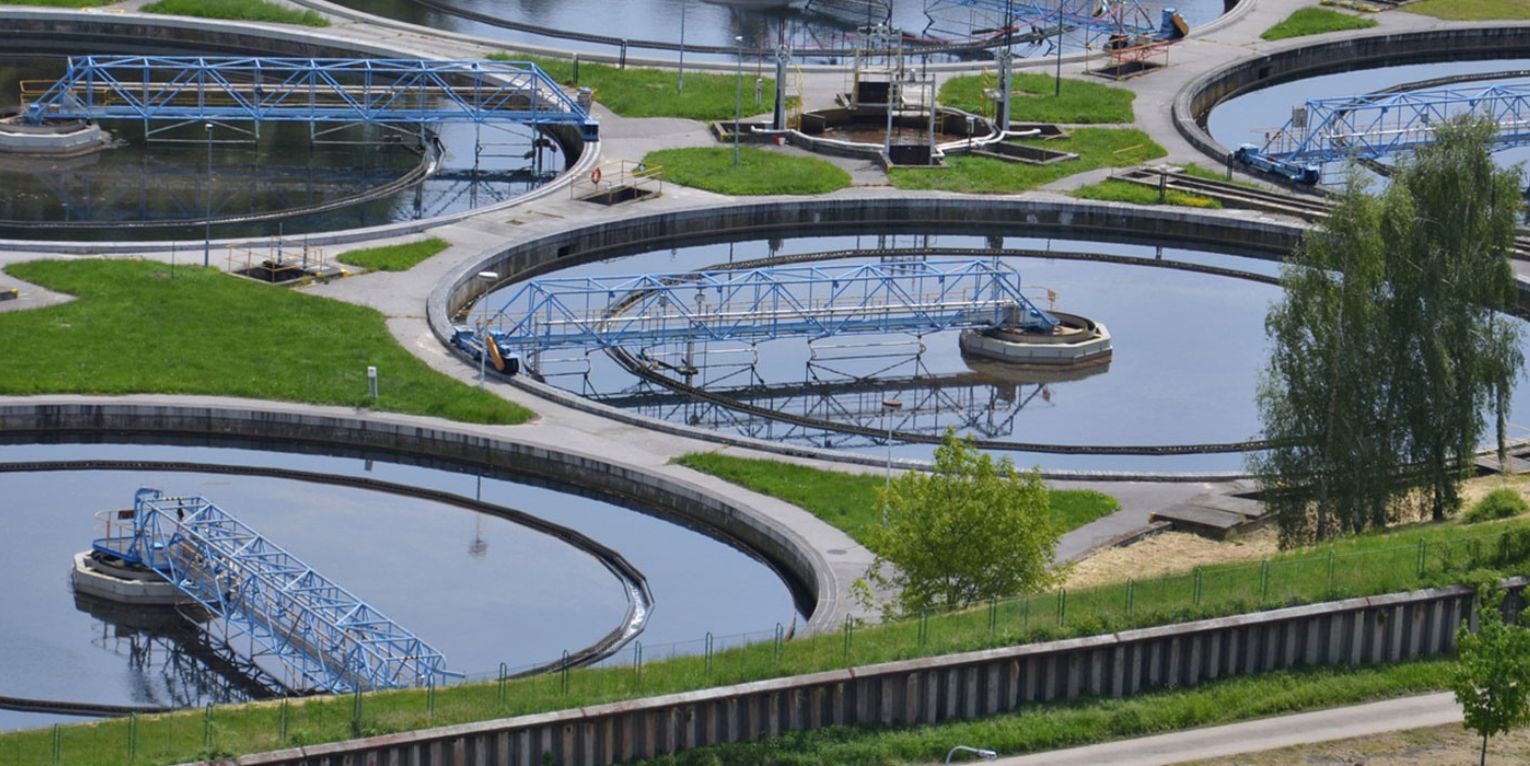
Wastewater treatment is the process by which wastewater is treated to make it usable in applications like industrial processes, irrigation, and even recreation. This helps maintain the environmental flow of water, with the by-products or sludge generating nutrients and energy.
Sludge is the main by-product of wastewater treatment, and it’s typically a mix of trace chemicals, food waste, human waste, micro-organisms, and inorganic solids all held together by some water. Sludge is called wastewater solids before treatment and biosolids after treatment.
Industrial facilities can also produce sludge, fuel factories, paper factories, and food manufacturing facilities. Since the content of sludge differs by industry, some of it is permitted to enter a municipal sewer network to be treated alongside municipal sludge.
Understanding Sludge Stabilization
Sludge stabilization is reducing the easily-degrading sludge compounds, unstable, and energy-rich compounds found in sludge, as well as the high water content. A secondary goal of sludge stabilization involves minimizing the number of pathogens found in the sludge.
Depending on the intended outcome of the sludge stabilization, one of three methods can be used. The methods are thermal stabilization, chemical stabilization, and biological stabilization, which could be either aerobic or anaerobic.
Thermal sludge stabilization makes use of heat. To achieve the desired outcome, combustion is typically applied to sludge that’s already been dried.
Chemical sludge stabilization involves increasing the pH level of the sludge to about 12 by adding lime to stop biodegradation.
Anaerobic biological sludge stabilization involves stabilizing the sludge under mesophilic conditions, while the aerobic method can take place either separately or simultaneously. In the separate process, the primary and excess sludge gets thickened separately from the wastewater treatment and is stabilized for 10 to 15 days. In the simultaneous process, the wastewater treatment is done at the same time as the stabilization of the raw sludge. This usually calls for a retention period of a minimum of 25 days.
Importance of Sludge Stabilization in Wastewater Treatment
Sludge stabilization plays an extremely important role in the treatment of wastewater. During the process, many terms are used to refer to various parts of the process or resulting materials, and some of them are outlined below:
- Increased dry solids content, refers to the resultant dry content that’s the result of sludge thickening, whereby water content in the sludge is decreased with low energy input.
- pH regulation, which involves using various chemicals to ensure that the pH of the sludge is at a level that’s hostile to pathogens in order to improve the quality of the various components of the sludge, both dry and wet.
- Pathogen inactivation, which is typically processing the sludge under conditions that make it uninhabitable to pathogens that can cause diseases if allowed to multiply and spread.
- Odor control is a step done to minimize or get rid of the odor in the sludge altogether. This makes it easier to process the sludge to the final points.
- Volume reduction, when sludge undergoes treatment to decrease its water content, which results in volume reduction. This subsequently reduces the amount of sludge that must undergo further treatment stages.
- Landfill-ready refers to material that’s ready to be taken to a landfill for disposal. This material has to satisfy all requirements in place to ensure safety and hygiene standards have been met.
Risks of Uncontrolled Release of Sludge
The reason it’s crucial to control and stabilize sludge is that failure to do so can have a major negative impact on the environment as well as human health and safety.
Sludge can affect human health and safety by causing and spreading water-borne diseases.
The effects of unstable sludge on the environment include the excessive release of greenhouse gases, pollution of soil, and release of noxious fumes and gases.
These are some of the outcomes that sludge stabilization aims to avoid. If done the right way, sludge stabilization has many positive outcomes.
The Role of Sludge Stabilization in Sustainable Wastewater Treatment
Sludge stabilization ensures that sustainable water treatment is possible. This is because a majority of the components of raw sludge that could make it interact negatively with the environment and water bodies are safely removed. Under a controlled environment, toxic emissions are typically going to be taken care of.
Sludge stabilization contributes to a circular economy by enriching soils that have been depleted of nutrients by activities such as forestry and farming. The water that results from the process can also be used in agriculture and other industries. Last but not least, biogas emitted from the process can be used to power the process, with excess being left over that can be put to other uses.
Conclusion
Sludge stabilization improves an amazing process and makes it even more beneficial by lowering the adverse effects of sludge in the environment and giving rise to materials that can be put to good use. This is why it’s beneficial to look into a solid sludge stabilization system that can help you get the most out of your hard work. Sodimate can help you get the right system for your industry, working alongside you to ensure that you get the best outcome and manage the products safely and efficiently. Give us a call and our team of professionals will help you from start to finish.