Drinking water treatment is the process of turning river water into drinking water. Raw water can come from groundwater or surface water and is not always drinkable without treatment.
What results into drinking water treatment?
Many compounds must be removed before the water can be drunk. Indeed, raw water is cloudy and contains pollutants, pesticides, organic molecules that can be toxic for human beings. These elements come from soil, dissolution of rocks, anthropic activities (industry, agriculture…). It is therefore necessary to carry out numerous physical and chemical treatments in order to have good quality water that meets the standards in force.
The amount of treatment needed depends on the initial quality of the raw water. Groundwater will need less treatment because the soil will have already filtered this water and thus removed part of the pollution. However, it is more complicated to have an important production.
The different steps to produce drinking water:
The production of drinking water is done in several stages as shown in the following diagram:
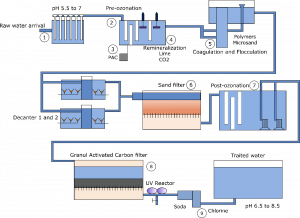
1) Water goes through physical pretreatment to remove anything that could damage the pumps, valves and other equipment in the drinking water plant. Large elements and sand are removed by a bar screen and a grit chamber.
2) Pre-oxidation: In order to remove mineral compounds (Fe, Mg), unpleasant taste and smell from the water, a strong oxidizer like ozone is used. It also allows to destabilize the dissolved organic matter and some micropollutants to facilitate the coagulation stage.
3) Accidental water pollution: Raw water can be accidentally polluted by pesticides, herbicides, surfactants, hydrocarbons. An injection of powdered activated carbon with a very high adsorbing power allows to eliminate a large part of these toxic elements.

4) Mineralization or Demineralization: Depending on the characteristics of the water, mineralization or demineralization is necessary.
-If the water hardness is too high a demineralization is needed to reduce the amount of Ca2+ and Mg2+ . The reduction of these elements will allow to limit the deposit of limescale that settles in the pipes and can damage water heaters and other household appliances.
-If the aggressiveness of the water is too high, mineralization is carried out to reduce the concentration of carbon dioxide which can attack the pipes and release toxic metals such as lead.
To ovoid these two problems, lime or soda ash is added to the water with different concentrations.

5) Coagulation Flocculation: In order to reduce water turbidity and to remove a large part of the undesirable dissolved elements a coagulant is added. It will create an agglomerate of dirt called floc that will grow and become heavier. To improve this process, a polymer and micro sand can be added to increase the weight and the size of the floc. In order to remove these flocs, the water will pass through decanters that will allow the flocs to settle to the bottom of the tank and be removed.
6) Sand filter: The clarified water passes through sand filters which are a porous environment allowing to retain the finest particles that did not settle in the previous stage such as the lightest flocs.
7) Ozonation: A new ozonation then is performed to kill bacteria, viruses and destroy the last organic molecules present in the water. Drinking water is subject to a very strict regulation on the acceptable quantity of bacteria, which means that it is imperative to eliminate all the pathogenic elements during this stage. Moreover, since ozone is a self-destructing gas and it does not present any risk to humans when used in this situation.
8) Granular activated carbon filter: This kind of filter can be used in case of chronic pollution or if there are too much biodegradable elements left in the water. These granular adsorbs the pollutants and the microorganisms living inside its pores can degrade these elements. In order to prevent these micro-organisms from entering the drinking water system, a UV reactor or ozone is used after the granular activated carbon filter to kill these bacteria.
9) Final step: Soda is injected to adjust the pH to between 6.5 and 8.5 and chlorine is added to avoid the bacteria and microorganism proliferation into pipes. The water is then stored in water tanks to give the chlorine time to work. After that, the water goes into a reservoir named a water tower to supply the inhabitants of the cities.
 In the end, more than 9 steps are necessary to produce drinking water that meets current regulations with mainly chemical treatments which requires facilities adapted to the type of raw water pumped.
In the end, more than 9 steps are necessary to produce drinking water that meets current regulations with mainly chemical treatments which requires facilities adapted to the type of raw water pumped.
To enjoy quality drinking water, give us a call at Sodimate, and we will be glad to guide you on the steps to take. Years of experience and a team of professionals will ensure to get exactly what kind of drinking water treatment facility will serve you for your industry, like pH control, Taste & Odor Control, Powdered Activated Carbon, or Water Softening & Remineralization.